The ProjBox Utility is a Windows or Raspberry Pi utility for generating electronic project enclosures. While these can always be drawn from scratch in a CAD program a simple generator may be more convenient. That is especially true if you stick to some standardized aspects.
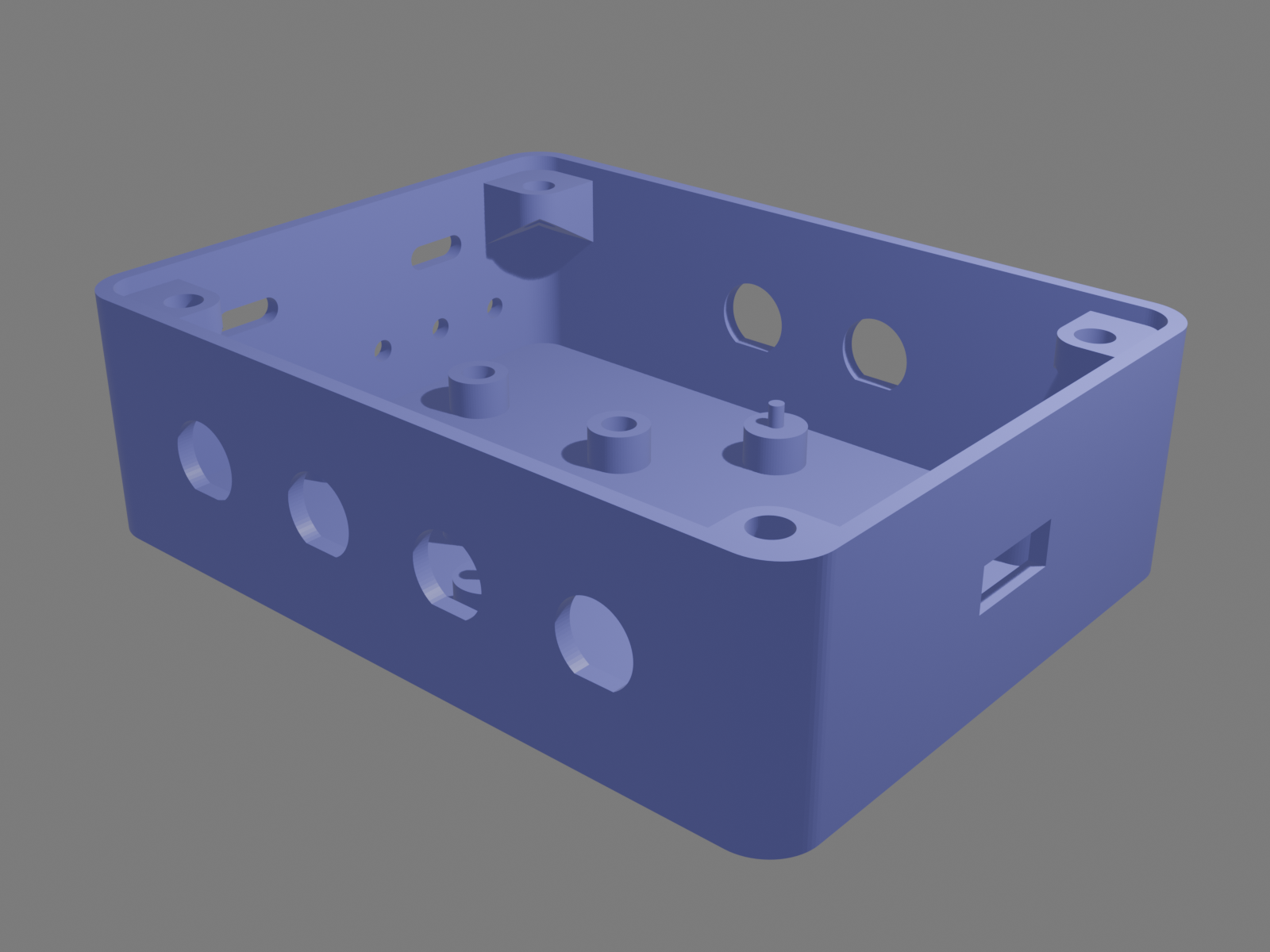
There are many community designs for project boxes that try to mimic commercial cast boxes. One reason not to just copy is that cast boxes are designed with sloping walls so as to be more easily removed from molds. A 3D printed box can and should be designed with perfectly vertical walls. Cast boxes also usually have screw posts for the cover extending all the way to the base. They could not be made any other way. A 3D printed box can, with care, be designed to have "hanging posts" just at the top of the box. Also, a custom 3D printed box can have hot threaded inserts and machines screws instead of self-tapping screws.
A design for a box is written as an .ini file with various parameters. For a simple case of "I need a box W x D x H with a hole on each end" the design is short.
One of the advantages of this approach is that the design is all visible and easily modified. You miscalculated something and it has to be wider? That's a simple text edit, a fraction of a second to generate the STL and a quick preview on your favorite software. You need to mount a PCB in the inside? Simple things are simple but there are ways to do complicated things too. In this case you just add/modify.
There are five styles of posts:
outerouter, inner, studouter, innerouter, inner, merged=yesouter, inner, merged=yes, clearThe slope parameter specifies the angle of the underside for hanging posts.
slope=0 will be flat, but print very sloppily.
slope=45 will be safe on almost all printers.
slope=30 is a reasonable compromise.
Posts by default are a set of four specified by two different ways.
If you specify with inset the posts are spaced from the inside corners.
This is useful if you might resize the box or copy the configuration for other size boxes.
The other way is by specifying width and height.
This will give you a rectangle of posts centered in the box.
Of course you can position this with xshift and yshift.
For a continuous post specify height.
If you specify relief that will reference the height to the top of the box.
This will make it more easily resizable.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| type | type | "post" |
| inset | length | distance from inside to post |
| xspan | length | X dimension of dual or quad layout |
| yspan | length | Y dimension of dual or quad layout |
| xshift | offset | position offset in X direction |
| yshift | offset | position offset in Y direction |
| outer | length | outer diameter of post |
| inner | length | inner diameter of hole in post |
| height | length | height of post or box |
| relief | length | distance from top of box to post |
| fill | length | distance from top to bottom of hanging post |
| clear | length | distance from bottom of hanging post to base |
| slope | angle | angle of bottom of hanging post in degrees |
| stud | length | length of stud on top of post |
| merged | bool | whether the post extends to be part of the wall |
There are four styles of holes:
diameterdiameter, flatdiameter, xstretch, ystretchwidth, heightHoles are by default centered in the middle of a flat section of wall.
Of course you can position them with xshift and yshift.
If you specify more than one hole in a side that side will first be divided into equal sections.
The individual holes will be centered in each section.
A common adjustment is to specify xshift=5 for the left hole and xshift=-5 for the right hole.
This will nudge the two closer.
When configuring for multiple holes it may be more convenient to divide a wall into unequal sections.
For instance, with three holes you might want to make the first and third sections bigger.
You can do that by increasing their "weight", weight=1.5.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| type | type | "hole" |
| inset | length | distance from inside to hole |
| xspan | length | X dimension of dual or quad layout |
| yspan | length | Y dimension of dual or quad layout |
| xshift | offset | position offset in X direction |
| yshift | offset | position offset in Y direction |
| diameter | length | diameter of round hole |
| flat | length | amount that a round hole is flattened |
| xstretch | length | elongation of hole in X direction |
| ystretch | length | elongation of hole in Y direction |
| width | length | width of rectangle hole |
| height | length | height of rectangle hole |
| bevel | length | bevel or countersink distance each side |
| align | align | left, right, top, bottom alignment |
| weight | weight | relative share when dividing a face |
A tile is a container for subdividing faces. Holes are implicitly placed in their own tile. A tile may be divided and laid out horizontally or vertically. A tile can contain holes, subtiles, posts or texts. Posts or texts are simply inserted in the plane of their parent body or tile.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| type | type | "tile" |
| layout | layout | horiz or vert |
| face | name | holes and posts on the tile |
| weight | weight | relative share when dividing a face |
Blocks are reference objects, like PCBs. You can enable them for viewing or disable them for slicing.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| type | type | "block" |
| width | length | width of block |
| depth | length | depth of block |
| height | length | height of block |
| xshift | offset | position offset in X direction |
| yshift | offset | position offset in Y direction |
| zshift | offset | position offset in Z direction |
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| type | type | "box" |
| sides | sides | number of sides |
| width | length | width of box |
| depth | length | depth of box |
| height | length | height of box |
| radius | length | outside radius of corner of box |
| base | length | thickness of bottom side |
| walls | length | thickness of walls |
| inside | name | holes and posts on the inside |
| bottom | name | holes and posts on the bottom side |
| front | name | holes in the front side |
| right | name | holes in the right side |
| back | name | holes in the back side |
| left | name | holes in the left side |
| blocks | name | blocks to be added |
A cover is an optional top-level object.
Holes specified with inset will work properly in the corners.
By specifying zshift you can make it so a box stl file and cover stl file can be overlaid without fine tuning.
By slicing the cover will be aligned with the printer plate by the slicer software.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| type | type | "cover" |
| sides | sides | number of sides |
| width | length | width of cover |
| depth | length | depth of cover |
| radius | length | outside radius of corner of cover |
| base | length | thickness of cover |
| top | name | holes and posts on the top side |
| bottom | name | holes and posts on the bottom side |
| xshift | offset | position offset in X direction |
| yshift | offset | position offset in Y direction |
| zshift | offset | position offset in Z direction |
This is a useful program, but not sophisticated. Some capabilities are limited. Posts may be placed on any surface, but will usually be placed on top or bottom of base layers. Incorrect parameters will cause the posts to be floating in space beyond the object of interest, but not geometrically illegal.
Holes are more complicated as holes disturb the underlying structure. Holes can only be inserted in a clean rectangular area. Multiple holes can be made by dividing a larger rectangular area into smaller pieces. The default is for this division to be along the (local) X direction (horizontal). By using tiles we can insert a section with (local) Y direction (vertical). An embedded tile inside that will use horizontal layout.
Inset holes present a special problem. Inset holes use up the corners in a cover. The remaining four-armed cross shaped area is available for discrete holes. Since we can only work with rectangular areas the question is whether to scrap the top and bottom sections and use the wide middle section or to scrap the left and right sections and use the tall middle section. As always, the horizontal layout is the default. If we want to use the tall middle we need to specify the original inset holes, a single tile and no direct holes. This will communicate that we want the tall middle section.
Download projbox.exe for Windows.
Download projbox for Raspberry Pi.